Exercise Intensity
• Refers to how hard you are working during exercise.
• Can be measured in a number of ways, the three that we have used so far are: 1) physical perception (how you feel), 2) rating of perceived exertion (RPE) scale and 3) the talk test. Revisit the RPE handout from class # 2 to review the RPE scale and better understand what constitutes moderate and vigorous intensity.
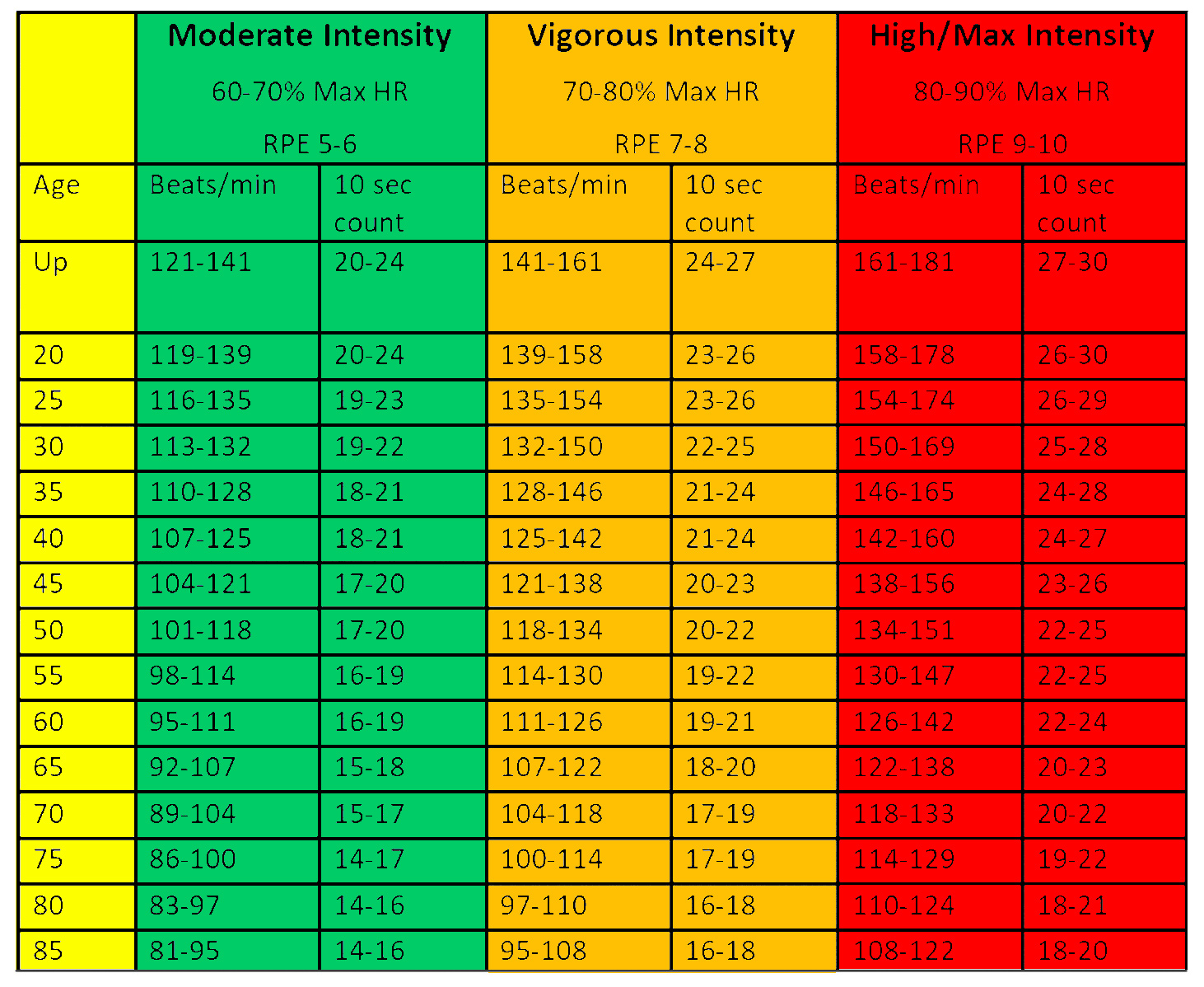
• Now lets’ add heart rate as a way to assess exercise intensity. Use the handout to quickly assess your target heart rate zone for moderate and vigorous intensity exercise.
Interval Training
• One of the most effective ways to improve your health and fitness.
• Can be done in less time which is perfect for our busy schedules.
• Anyone can build interval training into their routine, it doesn’t have to be all-out maximal intensity exercise to be effective.
• Anytime you can rev up the intensity above what you normally do, anywhere from 20 seconds to 2 minutes at a time, you are challenging your body to get more fit faster, and to burn more calories – both during exercise and throughout the rest of the day.
• Try this during your aerobic exercise part of the workout today.

The Benefits of Interval Training
• Your body burns more total calories in an exercise session.
• Your body continues burning calories at a higher rate many hours after exercise.
• You get fitter faster.
• You stay engaged and motivated during your workout, less likely to get bored.
Remember the exercise guidelines for how much exercise is recommended each week for good health. Aim to do a variety of things you enjoy – the list of options for ways to be physically active is almost endless!