Week 5
Portion Control and Reading Food Labels
HOW CAN I MEASURE THE FOODS I EAT?
Reading labels, as well as weighing and measuring foods, can help raise awareness of what we are eating. Creating a balanced diet with appropriate portions is important for weight loss and healthy eating habits.
Week 5
Portion Control and Reading Food Labels
HOW CAN I MEASURE THE FOODS I EAT?
Reading labels, as well as weighing and measuring foods, can help raise awareness of what we are eating. Creating a balanced diet with appropriate portions is important for weight loss and healthy eating habits.
Serving size vs. portion size
• A serving is a measured amount of food or drink, such as one slice of bread or one cup of milk.
• A portion is the amount of food you choose to eat. Many foods that come as a single portion actually contain multiple servings.
Altman Rule provides a quick and easy way to assess a food choice:
Grams of Protein + Grams of Fiber > Grams of Sugar
MEASURING UTENSILS
• Use metal or plastic cups and spoons. Level the contents off using a butter knife. Read the line at eye level.
• A food scale is also an easy way to measure hard-to-measure items. Use to measure servings of snack foods, vegetables/fruits , meats, etc. Weigh meats after they are cooked.

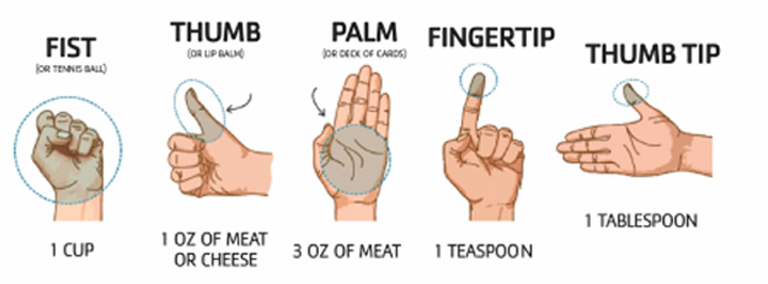
HAND METHOD
We can use our hand to estimate portion sizes. It is not perfect but can give us an idea of the amount of food we are eating if measuring tools are not available.
THE PLATE METHOD
Review the Harvard Healthy Eating Plate from Week 3.
The plate method helps to divide the plate to create a balanced meal. Your plate should be ¼ protein, ¼ starch and ½ vegetables and fruits (mostly vegetables). Add a small serving of dairy or healthy fat/oils.
Add more vegetables and some fruit to meals in place of starches. Aim for grains to be whole grains.
Week 5
HYDRATION AND HEALTHY BEVERAGE CHOICES
WHAT IS DEHYDRATION?
Dehydration is a decrease in total body water which occurs anytime that fluid intake doesn’t meet fluid loss. Water is the primary fluid in the body. However, the human body cannot store it, so it must be replaced every day.
THE ROLES OF FLUIDS
• Stay healthy and energized
• Regulates body temperature
• Aids digestion
• Carries nutrients around the body
• Cushions organs and joints
• Aids in removal of toxins and waste
• Keeps bowels regular
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF DEHYDRATION
• Thirst
• Dry lips and mouth
• Tiredness
• Irritability
• Headache or Dizziness
• Increase in heart rate
• Dark, strong smelling urine
HOW MUCH SHOULD I DRINK?
The Institute of Medicine currently recommends 104 oz (13 cups) for men and 72 oz (9 cups) for women. A good indicator of hydration status is urine, which should be almost colorless. Drinking water also helps you to feel full, and avoid unhealthy snacking/overeating.
TIPS TO STAY HYDRATED
• Drink a glass of water when you wake up each morning and before you go to bed.
• Carry a refillable bottle of water with you throughout the day.
• Keep a glass of water by your desk or on hand where you work.
• Make sure you have a drink with each meal, snack and medication.
• Don’t ignore thirst. Drink fluids when you feel thirsty.
• Set a daily fluid goal.
• Vary your fluids to include water, naturally flavored waters, seltzer, tea and coffee.
• Add flavor to water such as fresh fruit, lemon, basil, cucumber slices or mint leaves.
FLUID CHOICES
• Avoid sugar sweetened beverages as much as possible.
• Choose beverages that do not contain calories and sugar.
• Sugar sweetened beverages have little nutritional value and can lead to weight gain
and as well as increased risk of diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease.
• Be cautious of what is being added to your tea and coffee such as cream, sugar
and added flavorings! Some sugary drinks contain as much calories as an entire meal!
Think of these drinks as an occasional treat and get a small size.